10. Osteochondritis Dissecans
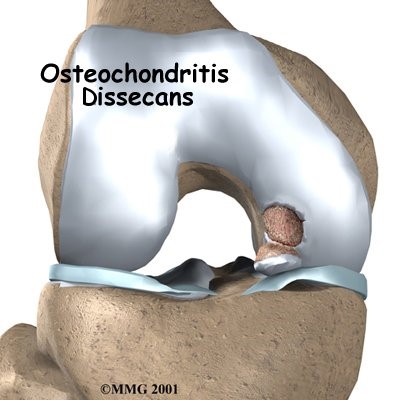
Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD) refers to a joint condition in which bone below the cartilage of a joint dies due to lack of blood flow. The dead bone and cartilage break loose causing pain and decreased joint movement. The condition can occur in any joint, but it most commonly affects the knee joint. Osteochondritis dissecans occurs most often in children and adolescents, especially those high actives in sports. The exact cause of OCD is unknown, but scientists suspect it might result from repetitive trauma to bone over time.
Symptoms of osteochondritis dissecans affecting the knee joint may include pain, swelling, tenderness, joint popping or clicking, joint weakness, and decreased the range of motion. Conservative measures such as rest and physical therapy are the mainstay of treatment for this disorder. Surgery may be needed for loose fragments in the knee joint or if conservative measures fail after 4 to 6-months.
