5. Bursitis
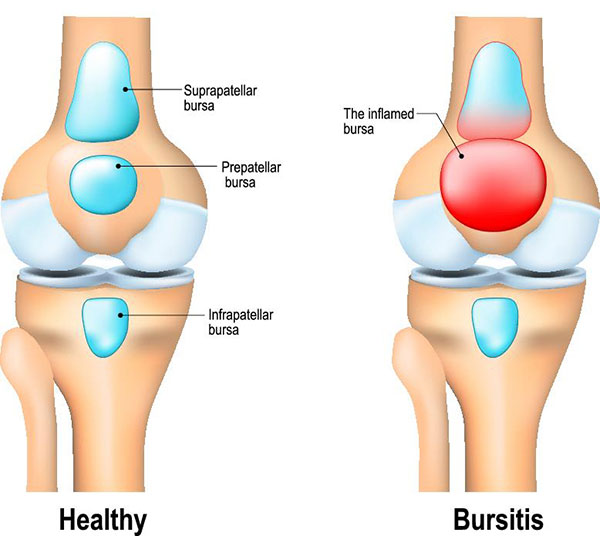
Bursitis of the knee refers to inflammation of a fluid-filled sac (bursa) located near the knee joint. A bursa reduces friction and serves as a cushion to reduce pressure between bones and tendons and muscles near joints. Causes of knee bursitis include frequent kneeling, a direct blow to the knee, the bacterial infection of a bursa, and complications from other conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout in the knee.
Common symptoms of knee bursitis include pain, warmth, tenderness, and swelling of the affected bursa. Treatment of knee bursitis may entail the use of anti-inflammatory medications or antibiotics (if an infection is present). Other treatment modalities utilized for knee bursitis may include physical therapy, steroid injection, and aspiration (drainage) of the bursa. Prevention of knee bursitis may be accomplished by wearing kneepads, taking breaks from prolonged kneeling, and avoiding excessive squatting.
